All you need to know about aluminum extrusion production
All you need to know about aluminum extrusion production
Aluminum extrusion is defined as the process of shaping material, by forcing it to flow through a shaped opening in a die.
Extruded material emerges as an elongated piece with the same profile as the die opening.
One process by which aluminum is forced into the tailor-made die and results in a constant cross-section that utilizes all the properties of the metal.
The aluminum extrusion process makes the most of aluminum unique combination of physical characteristics.
Press size determines how large of an extrusion can be produced.
Extrusion size is measured by its longest cross-sectional dimension, i.e. its fit within a circumscribing circle.

You may wonder what process makes aluminum extrusion.
Here are the details information and step by step
Aluminum extrusion detailed production process
- I Mold process
The aluminum extrusion process really begins with the design process, for it is the design of the product — based on its intended use — that determines many of the ultimate production parameters.
Questions regarding machinability, finishing, and environment of use will lead to the choice of alloy to be extruded.
The function of the profile will determine the design of its form and, hence, the design of the die that shapes it.
Die design:
Aluminum extrusion is the final product of aluminum billets that are extruded through a die after heating
And the extrusion die is a device with high-precision specifications designed according to demand to extrude aluminum profile with the required specifications and cross-sections;
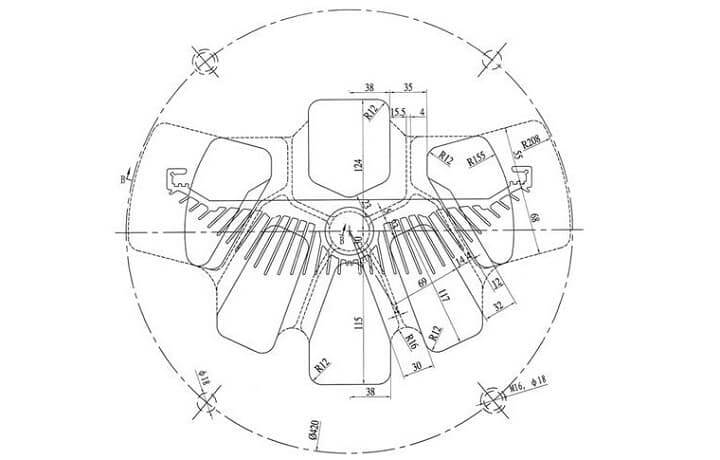
The principle and steps of mold design
1. Determine the design mold chamber parameters
First of all, when the designer gets the cross-sectional drawing, according to the extrusion ratio,
what is the maximum circumscribed circle of aluminum profile cross-section, and the complexity to determine which extrusion machine is suitable.
Set the size of the mold, if it is small, it will affect the service life and forming of the mold.
Generally speaking, the large section mold size is set to be larger, so that the mold is stable for production.
Set the distribution of mold porthole, feeder and solid mold design, working belt design, and molding holes design
2. Reasonable arrangement of die holes on the die
The so-called reasonable layout is to reasonably distribute single or multiple die holes on the mold,
So that the best metal flow uniformity can be obtained under the premise of ensuring the strength of the mold.
3. Reasonable calculation of die hole size
When calculating the die hole size, the main consideration is the chemical composition of the extruded alloy,
The shape and nominal size of the product and its allowable tolerance,
The extrusion temperature and the thermal expansion coefficient of the die material and the extruded alloy at this temperature,
And the cross-section of the product, the characteristics of the geometric shape and its changes during extrusion and stretching,
The size of the extrusion force and the deformation of the mold.
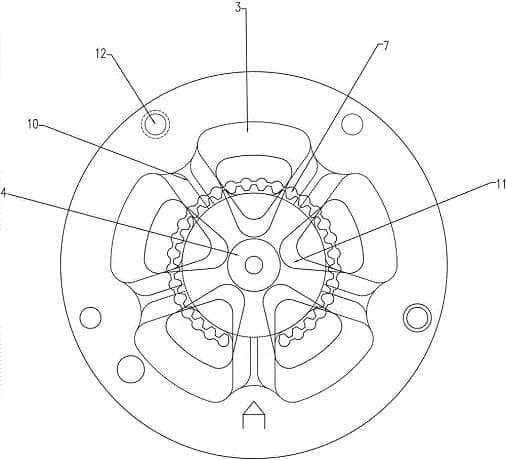
4. Reasonably adjust the metal flow rate
Generally speaking, the thinner the wall thickness of the profile is, the larger the circumference is, the more complex the shape will be, and the farther from the center of the extrusion cylinder, the shorter the die bearing should be.
When it is still difficult to control the flow rate with the die bearing, the shape is particularly complicated, the wall thickness is very thin, and the part far away from the center can be used of sprue spreader to accelerate the metal flow.
On the contrary, for those parts with much thicker walls or places very close to the center of the extrusion cylinder, the obstruction angle should be used to supplement the obstruction to slow down the flow velocity here.
In addition, you can also use process balance holes, process allowances, or use front chamber molds, and flow guide dies, and change the number, size, shape, and position of the portholes to adjust the metal flow rate.
5. Ensure sufficient mold strength
In addition to rationally arranging the position of the die holes, selecting the appropriate die material, and designing a reasonable die structure and shape,
it is also very important to accurately calculate the extrusion force and check the allowable strength of each section.
6. Clean and maintenance
The extrusion dies should be cleaned and inspected frequently.
If there are any problems, it should be repaired in time to avoid scratches, burrs and other hard injuries during the extrusion process of the profile, which will seriously affect the quality of aluminum extrusion.
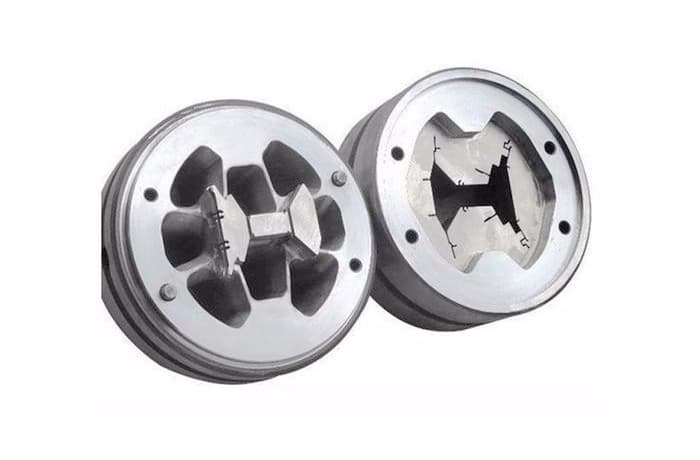

The extrusion die processing process flow chart
Solid die (structural profile without a closed cavity, not the porthole die)
Lathing → marking → Milling → Drilling → Grinding → Hardening → Tempering → Grinding of the surface → Fine milling of the guide channel → Wire cutting → EDM → Polishing → Clamping repairing → Acceptance → Test mold → Nitriding → Warehouse
Porthole die (structural profile with closed cavity)
Die backer
Turning → marking → Milling → Drilling → Grinding → Quenching → Tempering → Surface Grinding → Acceptance → warehouse
Die ring
Turning → marking → milling → drilling → grinding → quenching → tempering → plane grinding → fine turning → acceptance →warehouse
- II Melting process
6 series Alloys and their application

6005: Extruded profiles and pipes, used for structural parts that require strength greater than 6063 alloy, such as ladders, TV antennas, etc.;
6009: car body panels;
6010: thin plate, car body;
6061: Various industrial structures that require certain strength, weldability and high corrosion resistance, such as pipes, rods, and shapes for the manufacture of trucks, tower buildings, ships, trams, fixtures, mechanical parts, and precision machining , Sheet;
6063: Building profiles, irrigation pipes and extrusion materials for vehicles, benches, furniture, fences, etc.;
6066: Forgings and welding structure extrusion materials;
6070: Heavy-duty welded structures and extrusion materials and pipes used in the automotive industry;
6101: High-strength bars, electrical conductors and radiator materials for buses;
6151: Used for die forging crankshaft parts, machine parts and production of rolled rings, for applications that require good forgeability, high strength, and good corrosion resistance;
6201: High-strength conductive rods and wires;
6205: Thick plates, pedals and high impact resistant extrusions;
6262: Threaded high-stress parts requiring corrosion resistance better than 2011 and 2017 alloys;
6351: Extruded structural parts of vehicles, pipelines for water, oil, etc.;
6463: Building and various appliance profiles, as well as automotive decorative parts with bright surfaces after bright dipping and anodizing treatment;
6060, 6063, 6063A, 6463, and 6463A are often used in the production of building profiles,
and 6463A alloy is exclusively used for the production of bright silver aluminum profiles (mirror-like look).
6063A alloy is often used in the production of architectural profiles that require slightly higher strength than 6063 alloy, such as curtain wall materials.
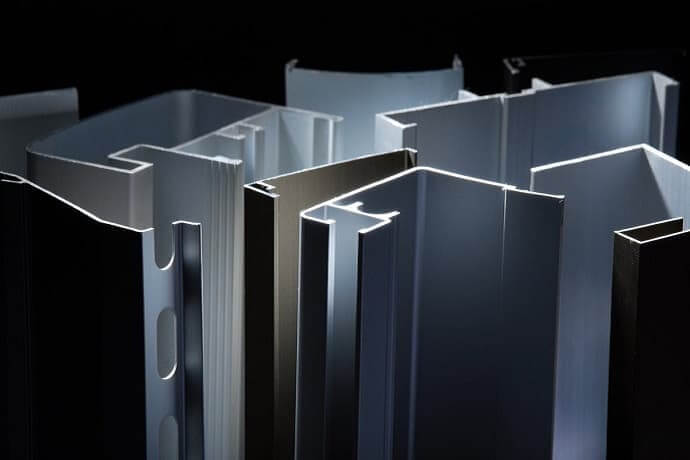

6061, 6082, 6106, 6005, 6005A, 6351 alloys are widely used in large structural parts that require good corrosion resistance, such as refrigerated container bottom plates, truck frame parts, and ship upper structure parts, railway vehicle structural parts and other mechanical structural parts.
6101 and 6101B alloys are used to produce aluminum alloy profiles for subway conduction.
6563 alloy is mainly used to produce radiator profiles.
2024, 5A02, 7005, 7020, and 7075 are high-strength alloys, which are mostly used in spacecraft, mechanical equipment, etc.
Melting processing flow chart
Materials→charging→melting→stirring→alloying→holding→degassing→refining→billet casting→homogenizing→cutting
Melting is the process of aluminum profile production.
According to raw materials and product structure, a reasonable choice of the aluminum profile casting process is the key to ensuring product quality, reducing energy consumption and improving production efficiency.
So what is the melting and casting process of aluminum profiles?
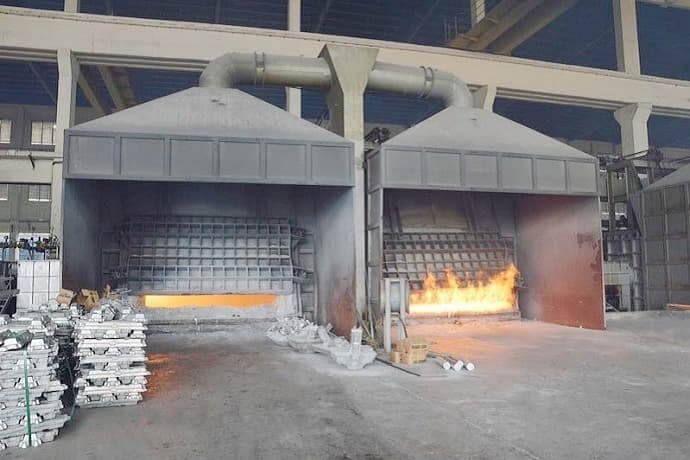

1. Aluminum ingots raw materials
Before production, according to different alloys and different quantities of aluminum billets demand, make aluminum ingots, magnesium ingots, silicon ingots, copper ingots and auxiliary materials ready in the workshop.
2. Melting charging
Use the forklift to charge the raw materials into the melting furnace.
3. Melting
After adding enough raw materials in the furnace, use natural gas to heat up to 700-730℃, and then the aluminum ingot will melt into a liquid state.
4. Refining
Adding agents to remove impurities in the molten aluminum.
5.Casting
25~35 seconds after the molten aluminum is filled with the distributor, the cooling water is turned on. The casting speed is 70~80% of the normal speed, and the speed is increased to the normal speed after falling 40-50mm.
6. Homogenization
Aluminum billets are subjected to secondary homogenization treatment.
7. Aluminum billets cutting
Remove the irregular parts at the front and back ends of the aluminum billets
8. Warehouse
Aluminum billets are bundled into the warehouse and placed.
Generally speaking, Aluminum melting is to turn aluminum ingots into aluminum billets, logs or other finished or semi-finished products through the process of alloying, stirring, standing, refining, and skimming.
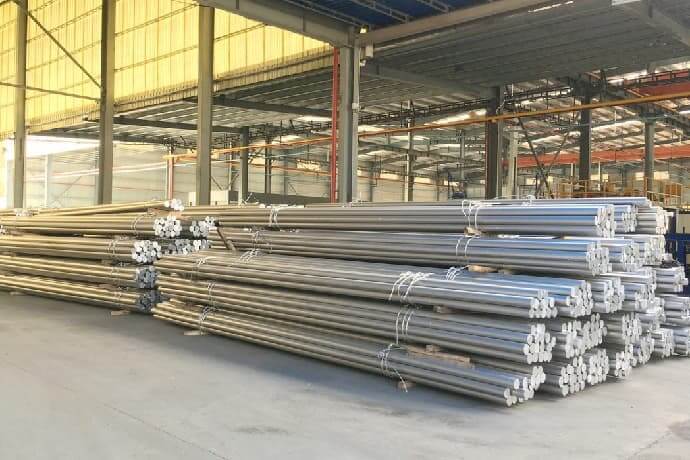

Melting and casting production is an extremely important process in the production of aluminum and aluminum alloy extrusion products.
The quality of aluminum billets directly affects the yield, quality and performance of aluminum extrusion products.
Now we get the billets for the extrusion, extrusion die and raw materials are ready for the extrusion.
- III Extrusion process
Aluminum extrusion – A process by which aluminum is forced into a custom-made die and results in a constant cross-section that utilizes all the properties of the metal.
As the extrusion molds were designed and the aluminum billets are available. All is ready for aluminum extrusion.
Aluminum extrusion process is a processing method that applies strong pressure to the metal billet placed in the die chamber (or extrusion cylinder),
forcing the metal billet to produce directional plastic deformation,
And extruding from the die hole of the extrusion die to obtain the desired section shape and size with certain mechanical properties parts or semi-finished products.
Types of the extrusion process
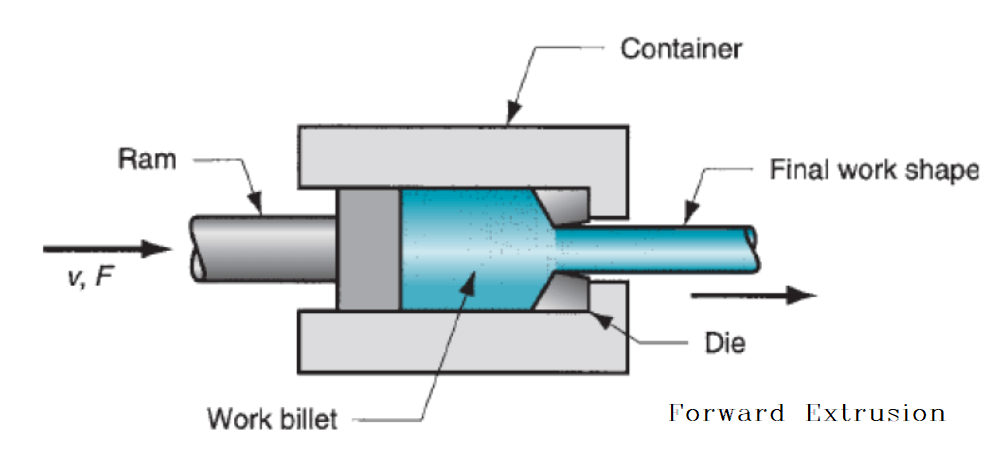
Forward extrusion
Forward extrusion, also known as direct extrusion, is the most common extrusion process. It works by placing the billet in a heavy-walled container.
The billet is pushed through the die by a ram or screw.
There is a reusable dummy block between the ram and the billet to keep them separated.
The major disadvantage of this process is that the force required to extrude the billet is greater than that needed in the indirect extrusion process because of the frictional forces introduced by the need for the billet to travel the entire length of the container.
Because of this, the greatest force required is at the beginning of the process and slowly decreases as the billet is used up.
At the end of the billet, the force greatly increases because the billet is thin and the material must flow radially to exit the die.
The end of the billet (called the butt end) is not used for this reason.[i]
[i] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extrusion
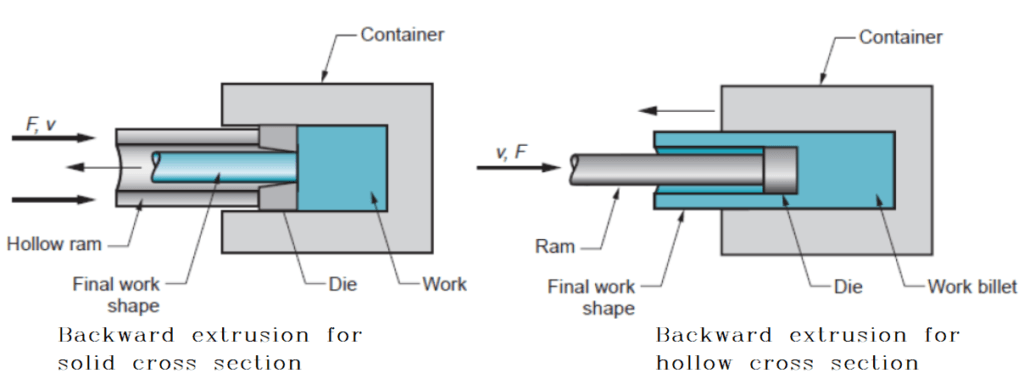
Backward extrusion
Backward extrusion, also known as indirect extrusion, the billet and container move together while the die is stationary.
The die is held in place by a “stem” which has to be longer than the container length.
The maximum length of the extrusion is ultimately dictated by the column strength of the stem.
Because the billet moves with the container the frictional forces are eliminated.
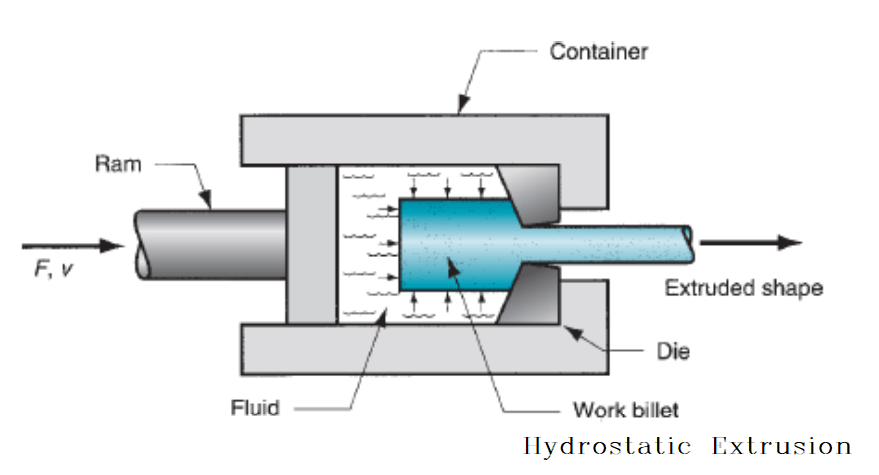
Hydrostatic extrusion
In the hydrostatic extrusion process, the billet is completely surrounded by a pressurized liquid, except where the billet contacts the die.
This process can be done hot, warm, or cold, however, the temperature is limited by the stability of the fluid used.
The process must be carried out in a sealed cylinder to contain the hydrostatic medium.
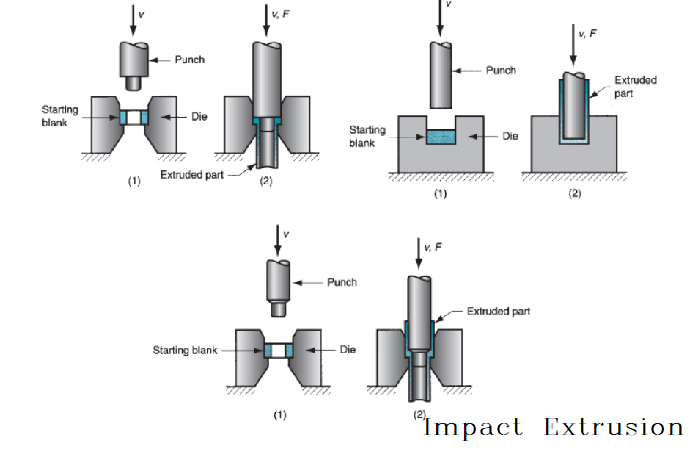
Impact extrusion
Impact extrusion is a manufacturing process similar to extrusion and drawing by which products are made with a metal slug.
The slug is pressed at a high velocity with extreme force into a die or mold by a punch.[i]
Impact extrusion is performed at higher speeds and shorter strokes than conventional extrusion.
It is used to make individual components. As the name suggests, the punch impacts the work part rather than simply applying pressure to it.
[i] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Impact_extrusion
Advantages of aluminum extrusion process
1. During the extrusion process, the extruded metal can obtain a more intense and uniform three-dimensional compression stress state in the deformation zone than rolling forging, which can give full play to the plasticity of the processed metal itself;
2. Extrusion process can produce not only rods, tubes, shapes, and wire products with simple cross-sectional shapes, but also profiles and tubes with complex cross-sectional shapes;
3. Extrusion process has great flexibility.
It only needs to replace the extrusion tools such as molds to produce products with different shapes, specifications and varieties on one equipment.
The operation of replacing extrusion molds is simple, fast, time-saving and efficient;
4. The precision of extruded products is high, the surface quality of the products is good,
and the utilization rate and yield of metal materials are improved;
5. The extrusion process has a good effect on the mechanical properties of the metal;
6. The process flow is short and the production is convenient. One-time extrusion can obtain an overall structure with a larger area than hot die forging or forming rolling.
The equipment investment is low, the mold cost is low, and the economic benefit is high;
7. Aluminum alloy has good extrusion characteristics and is particularly suitable for extrusion processing.
It can be processed by a variety of extrusion processes and a variety of mold structures.
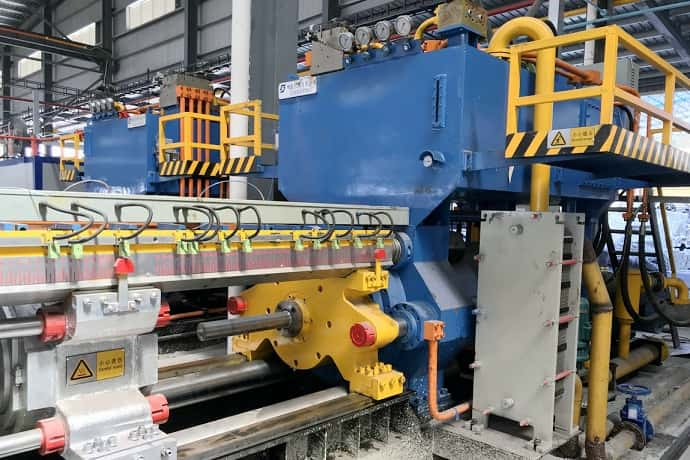

Step of the extrusion process
Aluminum billets→ Heating in the multi-billets heating furnace with hot log shear → the temperature reaches 480°C and the temperature is kept for 1h → the mold is heated to 480°C → the mold is placed in the mold base → feeding → extrusion → puller → straightening → aging → aging done→ cooling → complete
1. Place aluminum billets on the rack. Leave a certain gap between the aluminum billets.
Be careful not to stack the aluminum billets, otherwise, it will increase the difficulty of the operator and cause aluminum billets to fall and injure the staff during the operation;
2. Operate strictly in accordance with the process flow.
Place 12 aluminum billets in the furnace and heat them. When the heating time reaches 3.5h, the temperature reaches 480℃, and then the normal production can be carried out after heat preservation for 1h;
3. At the same time, put the extrusion die into mold heating oven and heat it to make the die temperature reach 480℃;
4. After the heating and heat preservation of the aluminum billets and mold is completed, put the mold into the mold base of the extrusion machine and prepare;
5. Put short aluminum billets into the raw material entrance of the extruder to prepare for extrusion;
6. Entering the extrusion stage. After the extruded profile comes out of the discharge hole, it is pulled by the puller, and then the length is determined for cutting, and then the aluminum profile is sent to the leveling table for straightening.
The aluminum profile can be transported to the finished product area for cutting to length.
7. Load the cut aluminum profile into the material frame according to the requirements, transport it to the aging area, enter the aging furnace, and perform the aging treatment.
8. After the aging temperature reaches 200℃, keep it for 2h, and then wait for it to be discharged from the furnace;
When it is discharged, it enters the cooling stage, which can be cooled by natural cooling or with a cooler.
At this time, the extrusion work is completed, and the extrusion of aluminum profiles with qualified appearance quality and shape and size is completed.
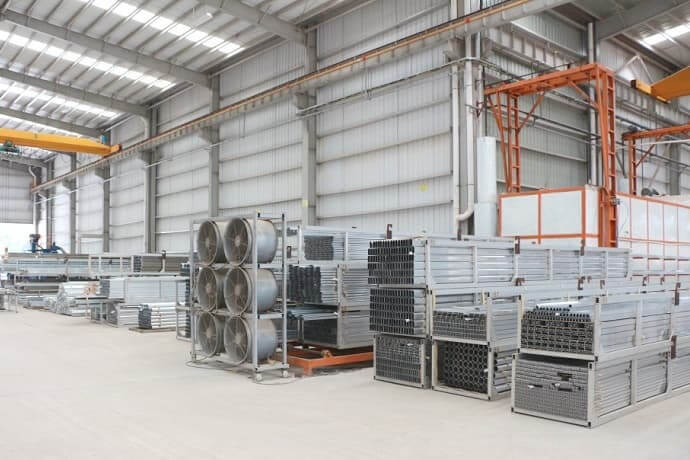

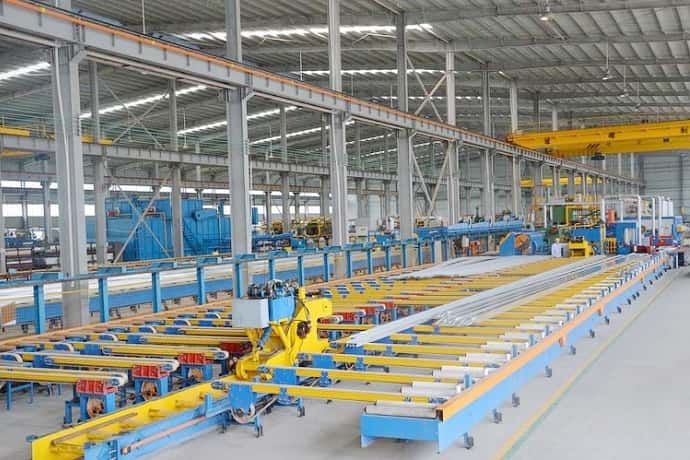
Aluminum extrusion will be carried out on an automatic production line consisting of billets heating, extrusion, cooling, tension straightening, sawing and other processes.
Equipment on the production line, including multi billets heating furnace with hot log shear, extrusion press, run-out table, stacker, profile conveyor, cooling bed, straightening machine, storage platform, puller, profile sawing machine, aging furnace, etc.
Honstar Aluminum Products Co., Ltd has been an aluminum industry leader for over 12 years in manufacturing precision aluminum parts, custom aluminum extrusions and standard aluminum extrusions.
We focus exclusively on producing the smallest, most complex, precision aluminum parts, custom aluminum extrusions, standard aluminum extrusions and floor covering aluminum profiles.
Contact us now for your aluminum profile order, and offer the total solution and one-stop service for your request.
Get A RELIABLE No-Obligation Quote










Everything is very open with a precise description of the issues. It was really informative. Your site is very useful. Many thanks for sharing. Whitney Alano Anet
Thank you for your kind comment.