What is a heat sink and its working principle?
What is a heat sink and its working principle?
Heat sink and its working principle
Every electrical and electronic component in a circuit generates some amount of heat while the circuit is executed by providing a power supply.
Typically high-power semiconducting devices like power transistors and optoelectronics such as light-emitting diodes, and lasers generate heat in considerable amounts and these components are inadequate to dissipate heat, as their dissipation capability is significantly low.
Due to this, heating up of the components leads to premature failure and may cause the failure of the entire circuit or system’s performance. So, to conquer these negative aspects, heat sinks must be provided for cooling purposes.
What is a heat sink and its working principle
What is a heat sink?
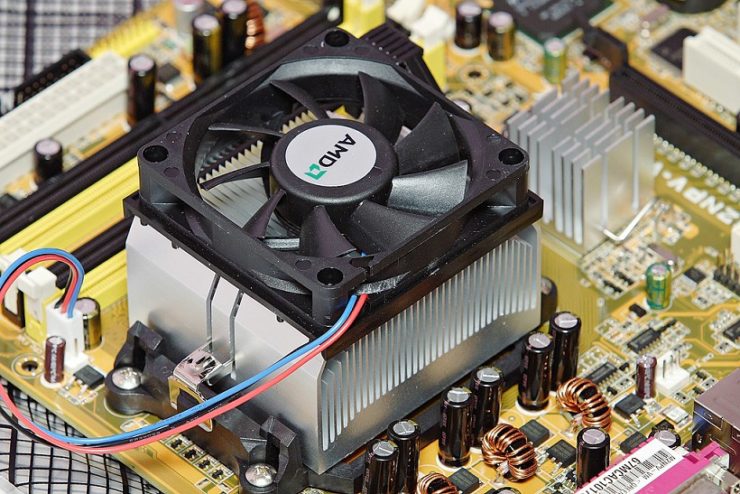
The heat sink is an electronic component or a device of an electronic circuit that disperses heat from other components (mainly from the power transistors) of a circuit into the surrounding medium and cools them for improving their performance, and reliability, and also avoid premature failure of the components.
For cooling purposes, it incorporates a fan or cooling device.
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is dissipated away from the device, thereby allowing regulation of the device’s temperature at optimal levels.
In computers, heat sinks are used to cool central processing units or graphics processors.
Heat sinks are used with high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the component itself is insufficient to moderate its temperature.
Heat sink working principle
Fourier’s law of heat conduction states that if the temperature gradient is present in a body, then the heat will transfer from a high-temperature region to allow- temperature region.
And, this can be achieved in three different ways, such as convection, radiation and conduction.
Whenever two objects with different temperatures come in contact with each other, conduction occurs causing the fast-moving molecules of the high-heat object to collide with the slow-moving molecules of the cooler objects, and thus, transferring thermal energy to the cooler object, and this is termed as thermal conductivity.
Similarly, heat sink transfers the heat or thermal energy from a high-temperature component to a low-temperature medium like air, water, oil, etc.
Usually, air is used as a low-temperature medium; and, if water is used as the medium, then it is termed as the cold plate.
Honstar Aluminum Products offers electronic cooling heat sink aluminum profile, amplifier heat sink aluminum profile and CNC Milled anodized aluminum heat sink for our customers. Total solution and one-stop service.









Comment *Thank you for helping me to understand that heat sinks are used to disperse heat from components that are used in a circuit. If I were to guess, I would imagine that a large machine with a lot of different electrical components would need multiple devices that absorb heat. As far as I know, heat can make a computer slow down and not run as efficiently as it could.